
Relational Databases
In today's modern world, we see that large language models and non-structured data tend to grab most of the news and capture public attention. However, much of the business world still uses structured data. Structured data is easy to visualize and understand. Furthermore, it lends itself naturally to predictive modeling as each record has the same properties. This means records can be easily selected any modeling techniques to identify correlation or information gain can be applied across all inputs.
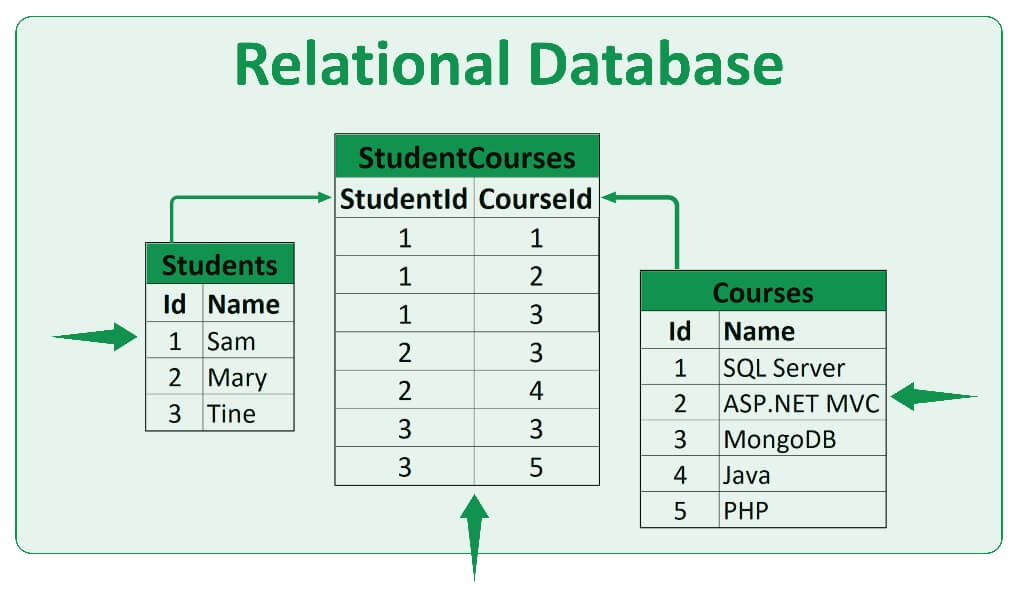
In my professional history, I have worked with a variety of relational database management systems (RDBMS). These come in different brands, but typically follow similar standards when it comes to data organization and efficiency tools. Data is accessed via Structured Query Language (SQL) queries, and can be browsed or returned in new objects (typically tables). These operations can display, subset, aggregate, and compare tables against each other in many different ways.
Many brands of RDBMS exist, and I have worked with the following in the past.- Teradata
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- IBM DB2